Optimizing Web Deployment with Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
Phyo Zin Wai / March 21, 2025
Introduction
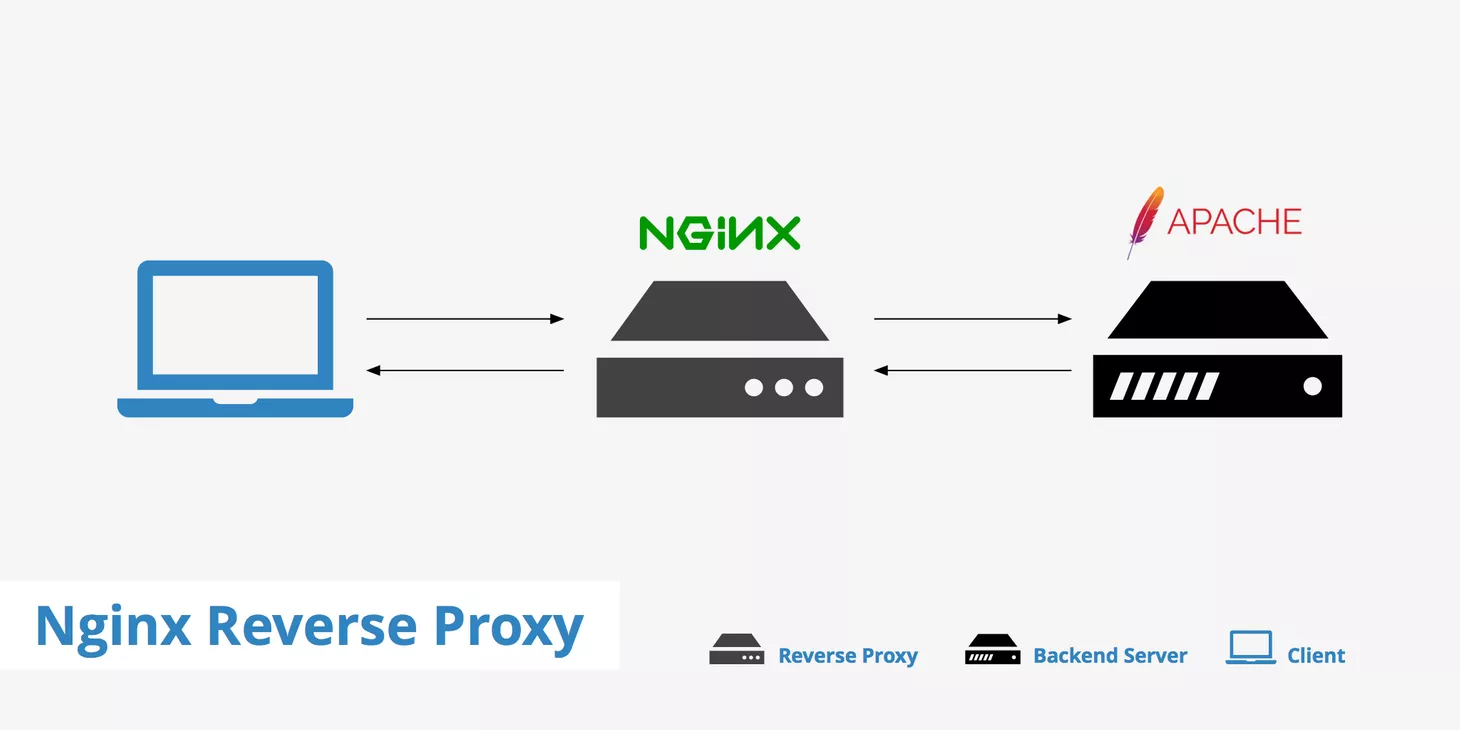
As a developer, deploying web applications efficiently is crucial for performance, security, and scalability. Nginx is a powerful web server and reverse proxy solution that helps route traffic, handle load balancing, and secure applications in production environments.
Why Use Nginx as a Reverse Proxy?
Nginx acts as an intermediary between clients and backend servers. This setup provides several benefits:
- Load balancing: Distribute traffic across multiple servers to enhance availability.
- SSL termination: Offload SSL encryption to improve backend performance.
- Caching: Reduce latency by storing static assets.
- Security: Protect applications by hiding backend services and filtering requests.
Setting Up Nginx as a Reverse Proxy
Installing Nginx
For Debian-based systems:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install nginx -yFor RedHat-based systems:
sudo yum install nginx -yAfter installation, start and enable the service:
sudo systemctl start nginx
sudo systemctl enable nginxConfiguring a Basic Reverse Proxy
To proxy traffic from Nginx to an application running on localhost:3000, create a configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/myappAdd the following:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}Enable the configuration and restart Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/myapp /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
sudo systemctl restart nginxLoad Balancing with Nginx
If you have multiple backend servers, Nginx can distribute requests among them:
upstream backend {
server 192.168.1.10:3000;
server 192.168.1.11:3000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}This configuration ensures incoming requests are balanced across multiple instances, improving reliability.
Securing Nginx with SSL
To enable HTTPS, obtain an SSL certificate (e.g., via Let's Encrypt):
sudo apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
sudo certbot --nginx -d example.com -d www.example.comThis automatically configures SSL for your site.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
1. Nginx Fails to Start
Check the error log for details:
sudo journalctl -xe | grep nginxRun a syntax check:
sudo nginx -t2. 502 Bad Gateway
This usually means Nginx can’t reach the backend service. Check if the application is running:
sudo systemctl status myappEnsure the firewall allows traffic:
sudo ufw allow 3000/tcpConclusion
Nginx is an essential tool for developers deploying applications. Whether you're using it as a reverse proxy, load balancer, or security layer, it enhances performance and reliability. By properly configuring Nginx, you can optimize deployments for scalability and security.